Lets start with simple opening, we dont talk about what is Fiddler , we talk about how to redirect all traffict to proxy.
Login as root first.
1
| user@ubuntuserver:/home/user# sudo su
|
First we need download redsocks and iptables in the Linux VM.
Use this command apt install redsocks iptables -y
1
| root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# apt install redsocks iptables -y
|
Then simply apply this code bellow, you can customize it for what you need.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| iptables -t nat -N REDSOCKS
# Exclude local and reserved addresses
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
# Now we need to add a rule that will redirect all packets from our custom REDSOCKS chain to the local port, we will use the default one – 12345
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports 12345
# Redirect all HTTP and HTTPS outgoing packets through Redsocks
# iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDSOCKS
# iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDSOCKS
# Redirect all HTTP and HTTPS incoming packets through Redsocks
# iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDSOCKS
# iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDSOCKS
## Filter all traffic from the own host
## BE CAREFULL HERE IF THE PROXY-SERVER RUNS ON THIS MACHINE
iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j REDSOCKS
# Filter all traffic that is routed over this host
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j REDSOCKS
|
After all set, we need configure /etc/redsocks.conf
Here the default configuration :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| base {
// debug: connection progress & client list on SIGUSR1
log_debug = off;
// info: start and end of client session
log_info = on;
/* possible `log' values are:
* stderr
* "file:/path/to/file"
* syslog:FACILITY facility is any of "daemon", "local0"..."local7"
*/
log = "syslog:daemon";
// detach from console
daemon = on;
/* Change uid, gid and root directory, these options require root
* privilegies on startup.
* Note, your chroot may requre /etc/localtime if you write log to syslog.
* Log is opened before chroot & uid changing.
*/
user = redsocks;
group = redsocks;
// chroot = "/var/chroot";
/* possible `redirector' values are:
* iptables - for Linux
* ipf - for FreeBSD
* pf - for OpenBSD
* generic - some generic redirector that MAY work
*/
redirector = iptables;
}
redsocks {
/* `local_ip' defaults to 127.0.0.1 for security reasons,
* use 0.0.0.0 if you want to listen on every interface.
* `local_*' are used as port to redirect to.
*/
local_ip = 127.0.0.1;
local_port = 12345;
// `ip' and `port' are IP and tcp-port of proxy-server
// You can also use hostname instead of IP, only one (random)
// address of multihomed host will be used.
ip = 172.26.160.1;
port = 8888;
// known types: socks4, socks5, http-connect, http-relay
type = http-connect;
// login = "foobar";
// password = "baz";
}
redudp {
// `local_ip' should not be 0.0.0.0 as it's also used for outgoing
// packets that are sent as replies - and it should be fixed
// if we want NAT to work properly.
local_ip = 127.0.0.1;
local_port = 10053;
// `ip' and `port' of socks5 proxy server.
ip = 192.0.2.1;
port = 1080;
login = username;
password = pazzw0rd;
// kernel does not give us this information, so we have to duplicate it
// in both iptables rules and configuration file. By the way, you can
// set `local_ip' to 127.45.67.89 if you need more than 65535 ports to
// forward ;-)
// This limitation may be relaxed in future versions using contrack-tools.
dest_ip = 192.0.2.2;
dest_port = 53;
udp_timeout = 30;
udp_timeout_stream = 180;
}
dnstc {
// fake and really dumb DNS server that returns "truncated answer" to
// every query via UDP, RFC-compliant resolver should repeat same query
// via TCP in this case.
local_ip = 127.0.0.1;
local_port = 5300;
}
// you can add more `redsocks' and `redudp' sections if you need.
|
In the /etc/redsocks.conf configuration, edit ip port type inside redsocks { }
You can use nano or vim
1
| root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# nano /etc/redsocks.conf
|
Then edit this :
1
2
3
| ip = 172.26.160.1;
port = 8888;
type = http-connect;
|
this is our proxy configuration, if you dont know what the ip host (Windows host) inside VM, you can check it with CMD, type it ipconfig
Output is like this :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| C:UsersAdministrator>ipconfig
Windows IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter vEthernet (Default Switch):
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::bf56:d73a:13b2:84ef%27
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 172.26.160.1
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.240.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
Ethernet adapter vEthernet (WSL):
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::3100:e28a:3a04:80ad%36
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 172.20.48.1
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.240.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
|
After all set, restart the redsocks using pkill redsocks , then start again with redsocks
1
2
3
| root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# pkill redsocks
root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# redsocks
root@ubuntuserver:/home/user#
|
Try to execute command like curl or wget (make sure proxy is running)
execute curl with proxy : curl --proxy 172.26.160.1:8888 google.com
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# curl --proxy 172.26.160.1:8888 google.com
<HTML><HEAD><meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<TITLE>301 Moved</TITLE></HEAD><BODY>
<H1>301 Moved</H1>
The document has moved
<A HREF="http://www.google.com/">here</A>.
</BODY></HTML>
root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# curl --proxy 172.26.160.1:8888 anasfanani.id
root@ubuntuserver:/home/user#
|
Off course we can see the traffict in fiddler proxy because we set --proxy in curl
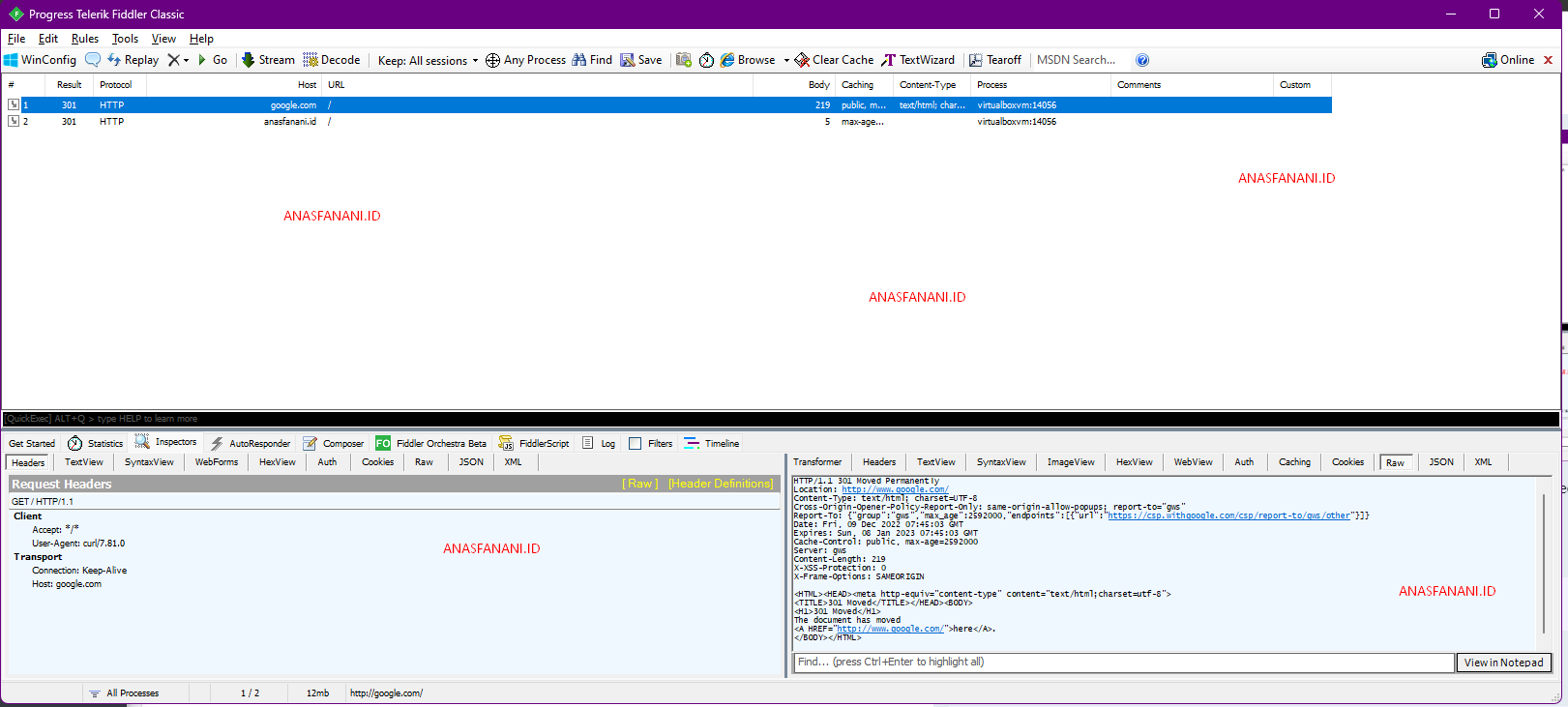
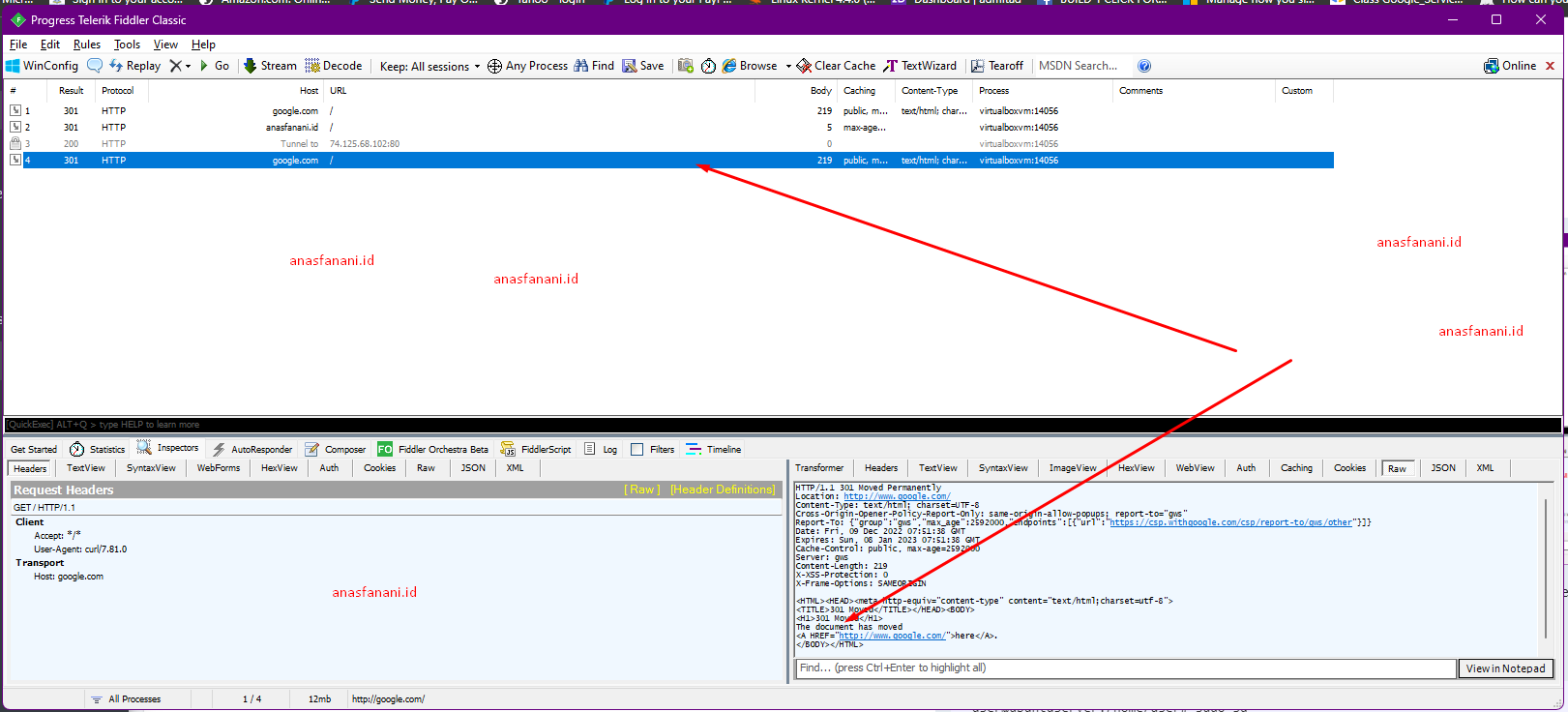
So lets use curl without --proxy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# curl google.com
<HTML><HEAD><meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<TITLE>301 Moved</TITLE></HEAD><BODY>
<H1>301 Moved</H1>
The document has moved
<A HREF="http://www.google.com/">here</A>.
</BODY></HTML>
|
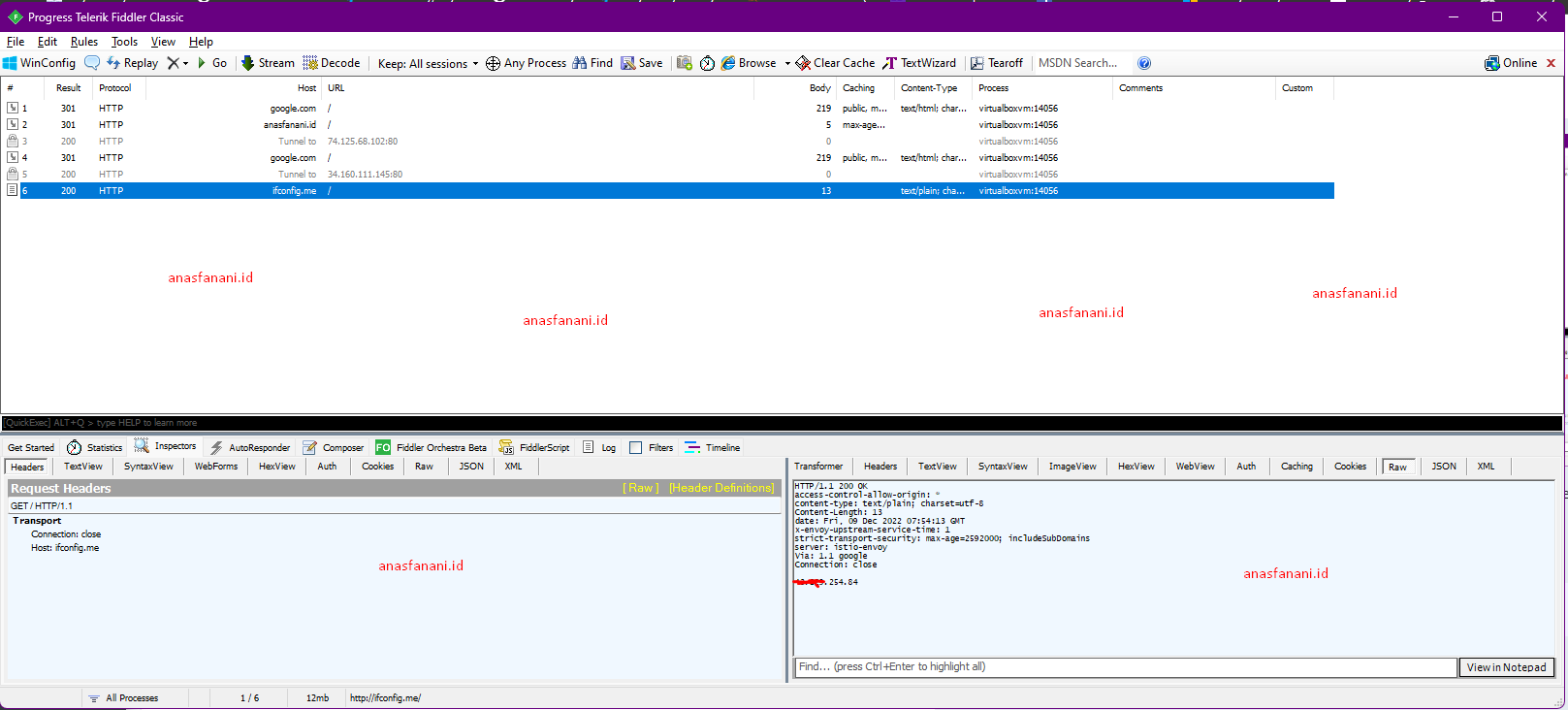
Lets use with other linux program like php , execute php -r "echo file_get_contents('http://ifconfig.me');" and see the Fiddler
1
| root@ubuntuserver:/home/user# php -r "echo file_get_contents('http://ifconfig.me');"
|
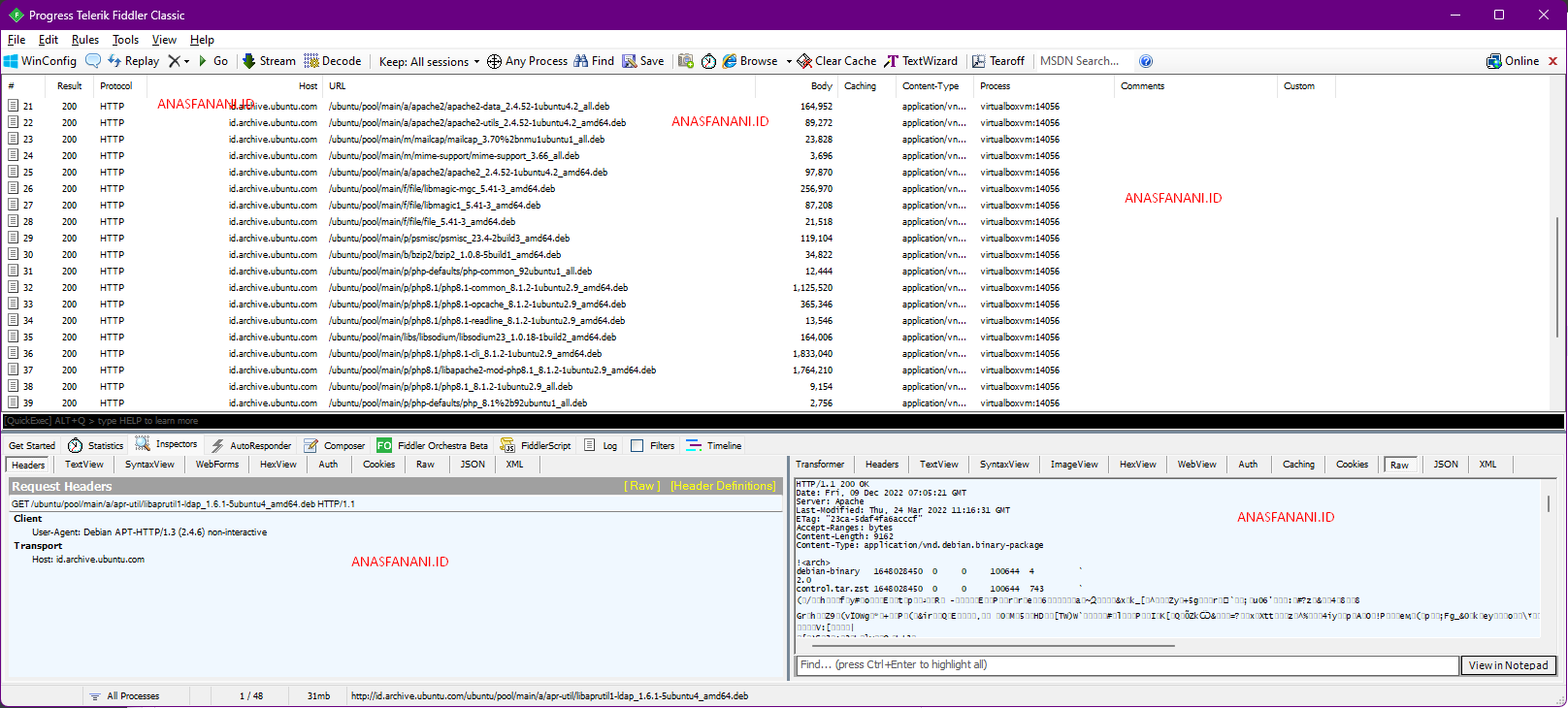
You can try see the packet from apt update or any other command.
All is set, simple, if you have questions, ask in comments. Thanks



